Understanding Organic Farming
Organic farming involves growing crops and raising livestock without synthetic chemicals. It’s rooted in principles of environmental stewardship and sustainability.
Definition and Principles
Organic farming avoids synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms. Farmers use natural processes to enhance soil fertility and control pests.
Key principles include:
- crop rotation
- green manure
- composting
- biological pest control
This approach aims to reduce pollution, conserve water, and promote biodiversity.
Historical Background
Organic farming has origins tracing back to early 20th century. Pioneers like Sir Albert Howard, Rudolf Steiner, and J.I. Rodale advocated for natural farming methods over chemical-based agriculture.
The movement gained traction in the 1960s and 1970s as environmental awareness rose. Today, organic farming is both a respected practice and a regulated industry, governed by bodies like USDA Organic in the United States.
Recent Developments in Organic Farming
Organic farming has seen significant progression in recent years, driven by technological advances, policy changes, and market trends.
Technological Advancements
Precision agriculture technologies now enhance organic farming efficiency. Farmers use drones for aerial imaging and crop monitoring, ensuring optimal plant health.
Advanced irrigation systems reduce water usage by targeting specific crop needs, improving productivity and resource management. Mechanical weeders replace chemical herbicides, maintaining soil integrity while controlling weeds.
Policy Changes
Policy shifts globally have bolstered organic farming. In 2020, the European Union’s “Farm to Fork” strategy aimed for 25% of agricultural land to be organic by 2030.
The USDA’s National Organic Program introduced stricter regulations, ensuring higher standards and transparency. These policy changes have incentivized farmers and reassured consumers about the authenticity of organic products.
Market Trends
The organic food market continues to expand. In 2021, the global organic food market reached $227 billion, a 12% increase from 2020. Consumer demand for organic products has risen due to health and environmental concerns.
Major retailers now allocate more shelf space to organic products, reflecting this demand. Online platforms specializing in organic goods also see growth, catering to a broader audience.
These developments highlight organic farming’s evolving landscape, driven by innovations and changing consumer preferences.
Insights from Recent Research
Recent research reveals crucial developments in organic farming, shedding light on its multifaceted impact on agriculture.
Soil Health and Biodiversity
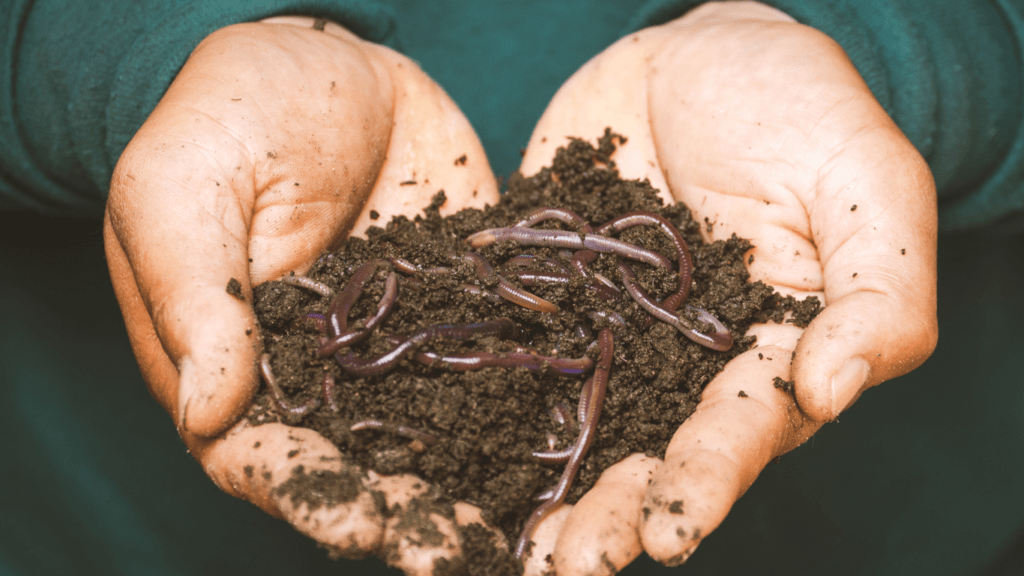

Research consistently shows that organic farming improves soil health. Studies conducted by the Rodale Institute demonstrate higher levels of soil organic matter and microbial activity in organically managed fields.
This heightened biodiversity enhances the resilience of crops to pests and diseases. Moreover, a 2019 study published in Nature Sustainability confirms that organic farms host 30% more species than conventional farms.
Crop Yield and Quality
While debates persist over crop yields, recent meta-analyses highlight that organic farming can achieve comparable yields under optimal conditions.
Data from FiBL and IFOAM’s 2021 report indicate that organic yields range from 80% to 100% of conventional yields. Interestingly, organic produce often shows higher nutritional value. For instance, research by British Journal of Nutrition in 2014 found that organic crops have up to 60% more key antioxidants.
Economic Viability
Economic studies reveal that organic farming can be financially viable. The USDA Economic Research Service reports that organic crops generally fetch higher prices, leading to increased profitability despite potentially higher production costs.
Furthermore, a 2020 analysis by the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements highlights that demand for organic products continues to rise, ensuring market stability for farmers committed to organic practices.
Challenges and Opportunities
Organic farming faces numerous challenges and opportunities. Addressing these aspects is crucial for sustainable growth in the sector.
Environmental Impact
Organic farming maintains a positive environmental impact by promoting ecological balance, soil health, and biodiversity. The absence of synthetic chemicals results in healthier soil and water. However, challenges exist, including lower crop yields and the need for more land compared to conventional farming.
Studies by the Rodale Institute show that organic farming systems can produce yields comparable to conventional systems under certain conditions, but require careful management and planning. Reducing emissions and improving water efficiency remain priorities for future advancements in organic farming.
Consumer Awareness
Increasing consumer awareness drives the demand for organic products. Many consumers now prefer organic food due to perceived health benefits and environmental concerns.
Challenges include misinformation and the higher cost of organic products, deterring some potential buyers. According to Statista, the global market for organic food reached $120 billion in 2020, reflecting growing consumer interest. Educating consumers on the benefits of organic products can help address misconceptions and expand the market.
Future Prospects
- The future of organic farming looks promising, with technological advancements and policy support paving the way.
- Drones and AI can enhance monitoring and planning, while government policies like subsidies and research funding provide necessary support.
- Challenges include ensuring organic integrity and dealing with climate change impacts.
- The USDA’s continuous updates to the National Organic Program regulations, along with initiatives like the EU’s “Farm to Fork” strategy, aim to bolster the organic sector.
- Collaboration between stakeholders, ongoing research, and consumer advocacy will shape the trajectory of organic farming.