Overview Of Farm-Based Renewable Energy
Farm-based renewable energy turns agricultural land into hubs of sustainable power generation. By harnessing solar, wind, bioenergy, and other technologies, farms produce clean energy directly on-site. This diversification of energy sources helps manage costs and secures energy independence.
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a reliable energy source even in rural, off-grid areas. Wind turbines capture wind energy, with each turbine capable of generating significant power depending on size and installation location.
Anaerobic digesters use organic waste from farm activities to produce biogas, which can then be converted into electricity or heat. This not only reduces waste but also creates a valuable energy byproduct. Bioenergy technology converts agricultural residues like crop leftovers and manure into biofuels, further expanding renewable energy sources on farms.
Deploying these technologies reduces reliance on fossil fuels and minimizes greenhouse gas emissions. Farms become more resilient to energy price fluctuations and contribute to environmental sustainability. By integrating these systems, farms transform into efficient, self-sufficient energy producers, aligning agriculture with renewable energy trends.
Solar Energy Solutions
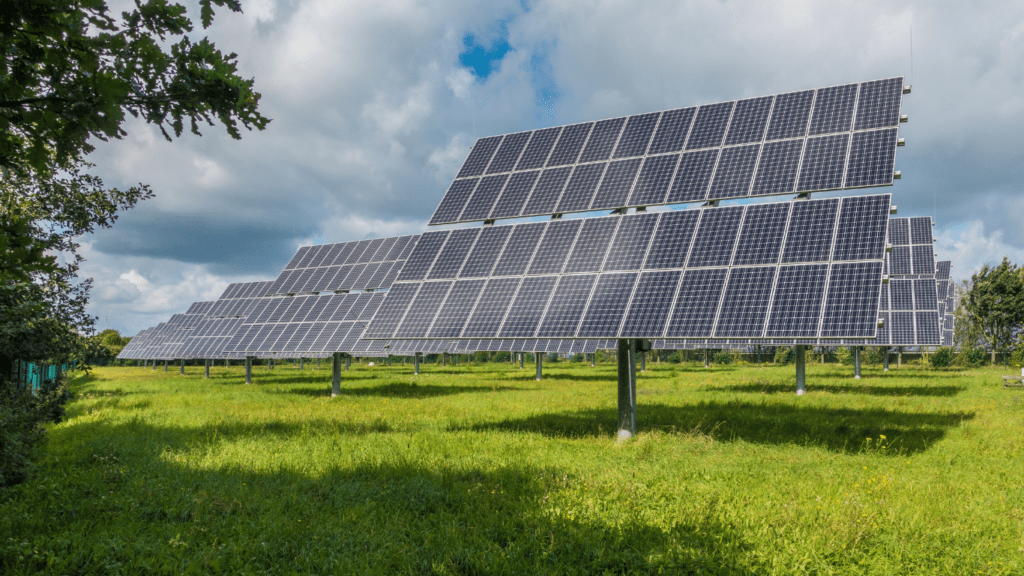
Farming operations increasingly adopt solar energy to enhance efficiency and sustainability. Solar technologies now play a significant role in modern agriculture.
Solar Panels
Solar panels provide an effective way for farms to harness and convert sunlight into electricity. These panels, typically installed on rooftops or open fields, can offset a farm’s energy consumption significantly. For example, a 5 kW solar panel system can produce about 7,000 kWh annually, powering lighting systems, machinery, and processing equipment.
State incentives and federal tax credits make solar panels more accessible, reducing initial costs and ensuring a quicker return on investment. Installation flexibility allows farmers to tailor solar arrays to specific energy needs, thereby optimizing performance.
Solar Water Pumps
Solar water pumps offer a cost-efficient and eco-friendly solution for irrigation and livestock watering. Unlike traditional pumps that rely on grid electricity or diesel fuel, solar water pumps operate using energy from solar panels, reducing operating costs.
These pumps ensure reliable water supply, especially in remote areas lacking electricity. For example, a solar-powered pump with a 1.5 kW system can move up to 6,000 liters of water per day, sufficient for midsize farms. Improved efficiency and reliability help farmers maintain crop health and livestock welfare without high energy expenses.
Wind Energy Technologies
Wind energy technologies also play a critical role in enhancing farm-based renewable energy initiatives. By harnessing wind power, farms can further reduce their dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Small-Scale Wind Turbines
Small-scale wind turbines, typically ranging from 1 kW to 100 kW, are ideal for farms with moderate wind speeds. These turbines can be installed on properties to generate electricity for various purposes.
For example, they can power irrigation systems, grain dryers, and electric fences. The key advantage lies in their ability to continually generate energy, provided there’s sufficient wind. Installation costs vary, but state and federal incentives often offset initial expenses.
Hybrid Wind-Solar Systems
Hybrid wind-solar systems integrate both wind turbines and solar panels, optimizing energy generation across different weather conditions. These systems provide a stable and continuous power supply to farms, even when either the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing. This dual approach ensures reliability.
For instance, solar energy can be harnessed during the day, while wind energy can be captured at night. Integration of these systems maximizes renewable energy use and minimizes the need for backup generators, ultimately leading to reduced operational costs.
Biomass Energy Innovations
Biomass energy innovations are transforming farms into sustainable powerhouses. These technologies utilize organic materials, cutting down waste and generating renewable energy.
Biogas Digesters
Biogas digesters convert organic waste into methane-rich biogas through anaerobic digestion. Manure, crop residues, and food waste serve as feedstocks for these systems. Farms can use biogas for heating, electricity, or as a natural fertilizer byproduct.
China and India have millions of small-scale digesters providing clean energy for cooking and lighting. In the US, larger farm-based digesters process thousands of tons of waste annually, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Farmers benefit from lower energy costs and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
Biomass Pellets and Briquettes
Biomass pellets and briquettes offer efficient ways to convert agricultural residues into fuel. These compacted forms of biomass include materials like wood chips, sawdust, and straw. Burning pellets or briquettes in specialized stoves or boilers generates heat and electricity.
Europe’s biomass pellet market supplies heating fuel for residential and industrial use. In the US, these products help farms utilize waste and reduce reliance on propane or natural gas. Biomass pellets and briquettes also lower carbon footprints and enhance energy security.
These innovations bolster the eco-sustainability of farms and their operations.
Advancements In Hydro Energy
Hydro energy technologies have significantly advanced, providing farms with sustainable energy solutions. This section covers two key technologies: micro-hydro systems and water wheels and turbines.
Micro-Hydro Systems
Micro-hydro systems allow farms to harness water flow for electricity. I see these systems as ideal for farms near streams or rivers. They convert water’s kinetic energy into electrical energy using small-scale generators.
Farms can produce up to 100 kW of power, enough to run various operations. By utilizing natural water sources, micro-hydro systems reduce dependence on grid electricity and minimize carbon footprint.
Several components comprise a micro-hydro system, including a turbine, generator, control system, and penstock. The penstock directs water to the turbine, which rotates generating electricity. This consistent energy supply benefits remote farms, slashing energy costs and improving sustainability.
Water Wheels and Turbines
Water wheels and turbines offer another effective way to generate hydro energy on farms. Water wheels convert flowing water into mechanical power. Traditional, simple designs are cost-effective and easy to maintain. Farms can use them for tasks such as grain milling and irrigation.
Modern turbines like:
- Francis
- Kaplan
- Pelton
increase efficiency. These turbines convert water flow into electricity, similar to micro-hydro systems but often on a larger scale. I notice that integrating water wheels and turbines enhances energy production, benefiting farms in various applications while promoting eco-friendly practices.
By adopting these advancements, farms can further enhance their renewable energy portfolio, reduce operational costs, and support environmental sustainability.
Economic And Environmental Benefits
Economic and environmental benefits of farm-based renewable energy technologies are substantial. These innovative solutions offer significant advantages, from cost savings to reducing carbon footprints.
Cost Savings
Adopting renewable energy on farms brings notable cost savings. Solar panels, solar water pumps, and wind turbines reduce reliance on expensive grid electricity, lowering monthly energy bills. Farms using biogas digesters also save on fuel costs by converting organic waste into usable energy.
The initial investment in renewable technologies, typically offset by reduced operational costs, pays off in a few years, making these technologies economically viable.
Reduction in Carbon Footprint
- Renewable energy technologies on farms cut carbon emissions.
- Solar panels and wind turbines generate electricity without burning fossil fuels, leading to cleaner energy production.
- Biogas digesters convert organic waste into energy, reducing methane emissions from decomposing waste.
- By integrating hydro systems, water wheels, or turbines, farms harness clean energy from water flows, further decreasing environmental impact.
- Farms adopting these technologies contribute to global efforts to combat climate change by minimizing their carbon footprint.



